If you’re struggling with student loan payments and feel like you’re stuck with a monthly payment that you cannot make, don’t fret!
There are tons of options available for student loan borrowers.
Even though you may have selected or were assigned a repayment plan when you first began repaying your student loan debt, you can change repayment plans at any time!
But with so many options available, it can be difficult to sort through them and ensure you’re on the right one. Here we offer you a student loan repayment plan comparison, so you can decide which one will work best for you and your current situation.
How Many Student Loan Repayment Plans Are There?
We understand that at first glance the options can be overwhelming. Standard vs Income Driven, Revised & Extended programs, what’s the difference between them all and what’s going to save you the most money?
When it comes to student loan repayment plans, you’re looking at 8 different options which are separated into 2 categories, Standard and Income Driven.
Both of these have 4 different repayment plans under their umbrellas.
Just click on the plans below in order to jump to information on that particular one:
- Income-Based Repayment Plan (IBR)
- Income-Contingent Repayment Plan (ICR)
- Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan (PAYE)
Revised Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan (REPAYE)- Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE) Repayment Plan
- Standard Repayment Plan
- Graduated Repayment Plan
- Extended Repayment Plan
- Extended Graduated Repayment Plan
What Student Loan Repayment Plan Is Best For Me?
There’s no blanket answer on which student loan repayment plan is best. These plans are designed to help people in just about every situation so it’s just a matter of seeing what fits you and your current circumstances.
If you’re interested in a lower monthly payment, an income-driven plan will be one of your best options. On the other hand, if you’re looking to get out of debt as quickly as possible- a standard repayment plan will be a better fit.
Let’s dive deeper into the specifics of each plan so you can figure out which one will be the best option for you and your current needs.
Standard Repayment Plans
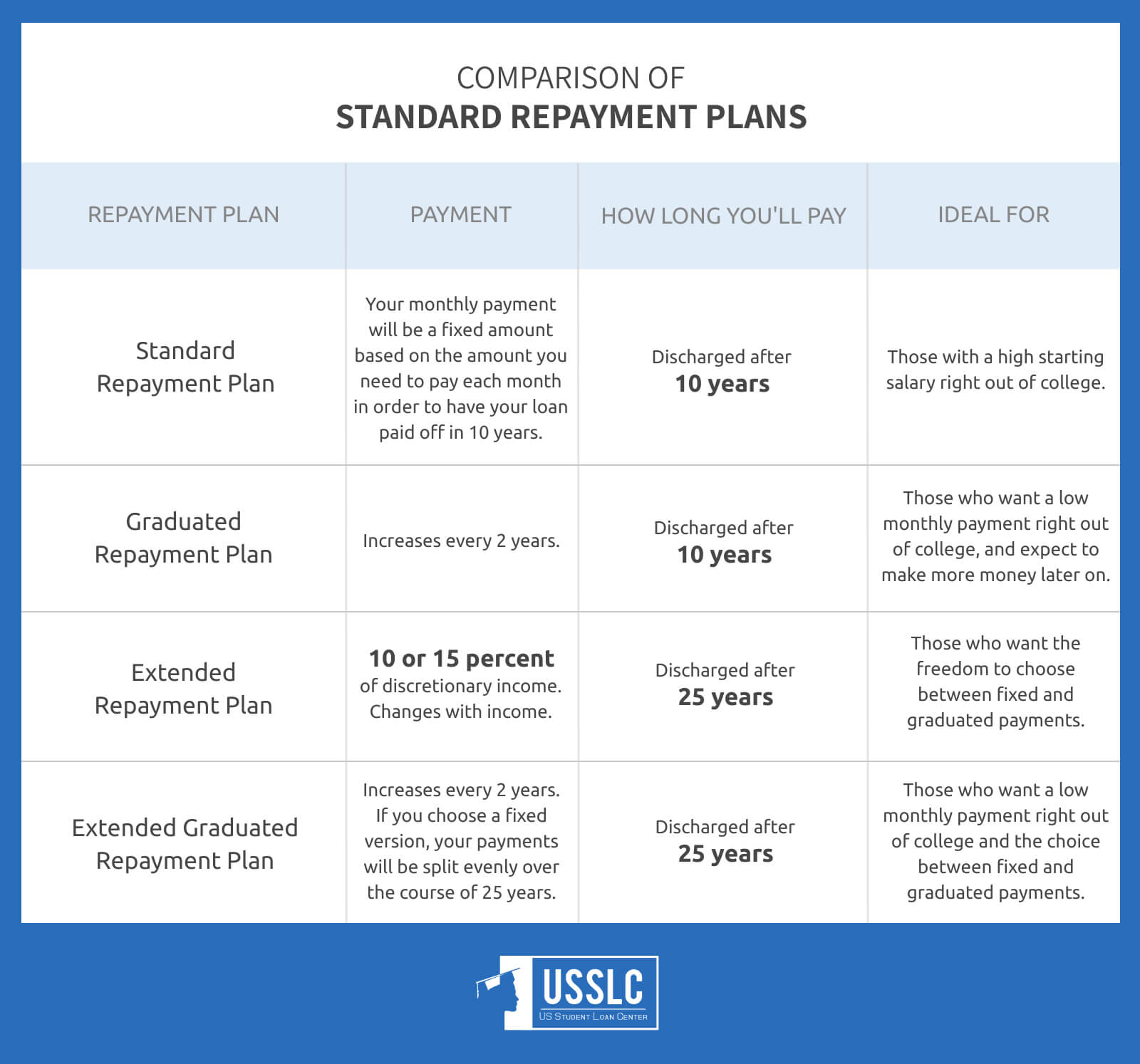
1. Standard Repayment Plan
Unless you’ve chosen a different repayment plan, you’ll automatically be placed into the Standard Repayment Plan by default when you graduate.
Plan Basics
The Standard Repayment Plan generally comes with the highest monthly student loan payment. This will be a fixed amount that ensures you’re debt free after just 10 years of payments.
Time Till Debt Free
10 Years
Loans Eligible for Standard Repayment
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans
- Direct PLUS Loans
- Direct Consolidation Loans
- Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans
- Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans
- FFEL PLUS Loans
- FFEL Consolidation Loans
Monthly Payments
Your monthly payment will be a fixed amount based on the amount you need to pay each month in order to have your loan paid off in 10 years. This will be calculated by dividing your total student loan debt into 120 payments. No matter what, you’ll be paying at least $50 a month. Although you should expect it to be higher.
Pros of the Standard Repayment Plan
- You’ll pay less interest for your loan over time than you would on any other plan.
- If payments are made as scheduled, this is the fastest way to pay off your student loan debt.
Cons of the Standard Repayment Plan
- The monthly payments on the Standard Repayment Plan are generally higher than the other plans available to you.
- If you’re not able to secure a high paying job right out of college, you’ll most likely not be able to afford the monthly payments.
2. Graduated Repayment Plan
This plan gives you a low initial monthly payment that increases in size every two years.
Plan Basics
The Graduated Repayment Plan provides you with a low initial monthly payment that increases in size every two years. Towards the end of the repayment period, your monthly payment typically ends up being more than it would under the Standard Repayment Plan.
Time Till Debt Free
10 Years
Loans Eligible for Graduated Repayment
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans
- Direct PLUS Loans
- Direct Consolidation Loans
- Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans
- Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans
- FFEL PLUS Loans
- FFEL Consolidation Loans
Monthly Payments
You’ll start off with a monthly payment that’ll remain consistent for 2 years. After that, your monthly payment will continue to increase every 2 years.
There’s a cap on your monthly payment which means that it’ll never be more than 3 times greater than your original payment. Your payment will also never be smaller than the amount of interest adding to your loan each month.
Pros of the Graduated Repayment Plan
- You’ll be debt free in just 10 years
- You’ll have a low monthly payment right out of college
Cons of the Graduated Repayment Plan
- You’ll pay more interest than you would under the Standard Repayment Plan.
- While you’ll have lower payments up front, it’s not so easy to predict whether your salary will increase as your payments do.
3. Extended Repayment Plan
This plan offers you a smaller monthly payment than you would receive on the Standard Repayment Plan.
Plan Basics
The Extended Repayment plan offers a fixed or graduated monthly payment that will be significantly less than what you’d pay on the Standard Repayment Plan. Since the monthly payment is lower, the payback period will be considerably longer.
Time Till Debt Free
25 Years
Loans Eligible for Extended Repayment
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans
- Direct PLUS Loans
- Direct Consolidation Loans
- Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans
- Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans
- FFEL PLUS Loans
- FFEL Consolidation Loans
Monthly Payments
If you choose a fixed payment, your monthly payment will remain the same every month.
If you choose a graduated payment, your monthly payment will start off smaller and gradually increase over the course of the repayment period.
Pros of the Extended Repayment Plan
- Your monthly payments will be lower than on the 10-Year Standard Plan.
- You have the flexibility to decide if you’d like your monthly payments to be fixed or graduated.
Cons of the Extended Repayment Plan
- You’ll pay more for your loan over time than under the 10-Year Standard Plan.
- The time it takes to pay back your loans will also be significantly longer.
4. Extended Graduated Repayment Plan
This plan is a variation of the Extended Repayment Plan.
Plan Basics
The Extended Graduated Repayment Plan lowers your monthly payments by lengthening your repayment term. Payments will start lower, based on how much you owe.
Time Till Debt Free
25 Years
Loans Eligible for Extended Graduated Repayment
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans
- Direct PLUS Loans
- Direct Consolidation Loans
- Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans
- Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans
- FFEL PLUS Loans
- FFEL Consolidation Loans
Monthly Payments
Your monthly payments will start small and increase every two years.
If you choose a fixed version of this plan, your payments will be split evenly over the course of 25 years.
Pros of the Extended Graduated Repayment Plan
- You’ll have a low monthly payment right out of college
Cons of the Extended Graduated Repayment Plan
- You’ll pay more for your loan over time than under the 10-Year Standard Plan.
- The time it takes to pay back your loans will also be significantly longer.
Income Driven Repayment Plans
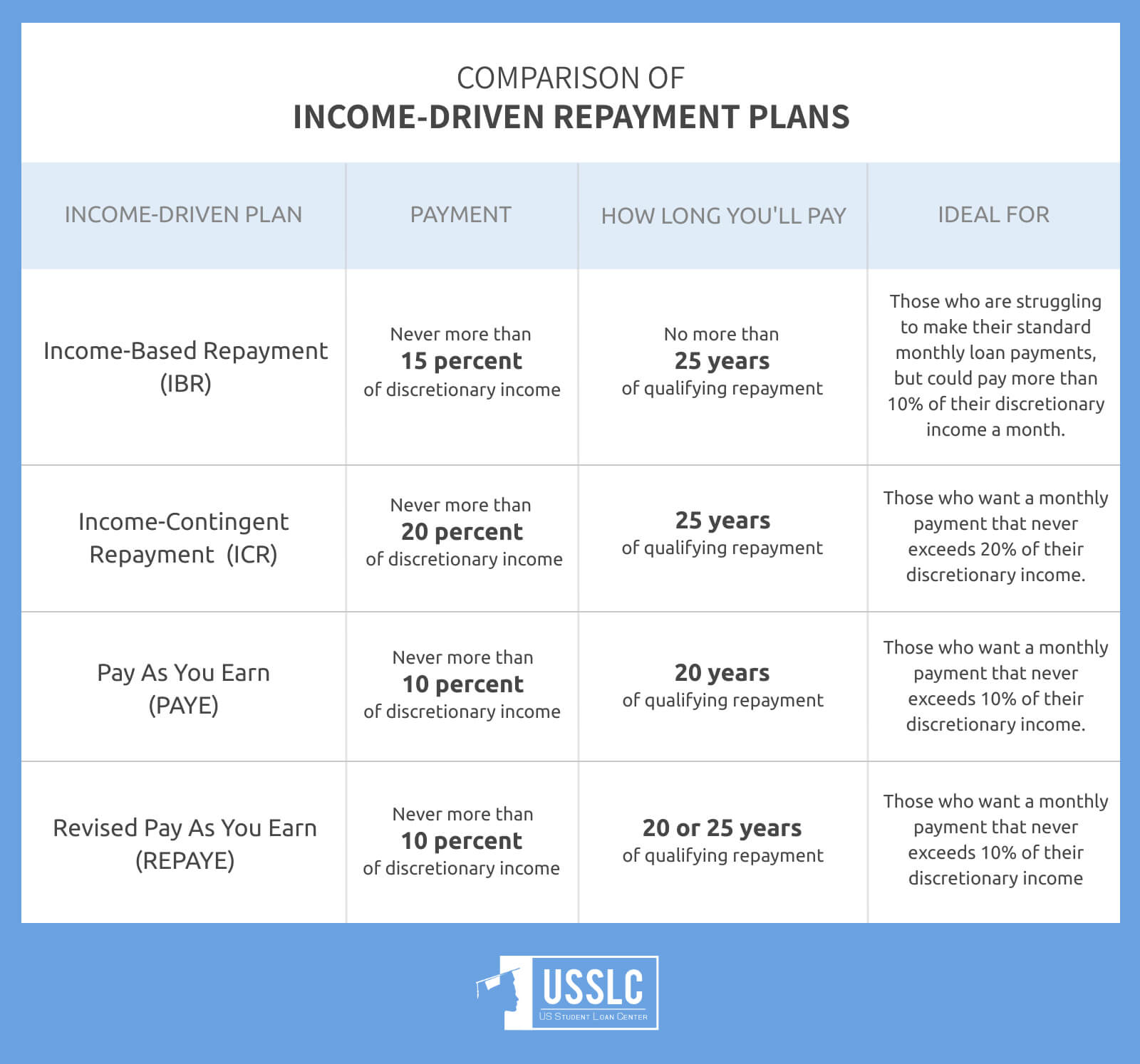
1. Income-Based Repayment Plan (IBR)
This repayment plan can help you get a more affordable monthly student loan payment based on your income and the size of your family.
Plan Basics
The Income-Based Repayment Plan calculates your monthly payment based on your income and the size of your family, while never exceeding 15% of your discretionary income. You’re not required to pay any interest that isn’t covered by your monthly payments for the first 3 years.
Time Till Debt Free
20 to 25 Years
Loans Eligible for Income-Based Repayment
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans
- Direct PLUS Loans made to graduate or professional students
- Direct Consolidation Loans that don’t include repaying Plus loans made to parents
- Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans (made under the FFEL Program)
- Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans (made under the FFEL program)
- FFEL PLUS Loans for graduate and professional students
- FFEL Consolidation Loans that didn’t repay any PLUS loans made to parents
- Federal Perkins Loans (*if they are consolidated)
Monthly Payments
Your payment is calculated by taking 15% (10% if you are a new borrower*) of the difference between your adjusted gross income (AGI) and 150% the poverty level for your state and family size.
Your payments change as your income changes.
Pros of the Income-Based Repayment
- Your monthly payments will be lower than on the 10-Year Standard Plan
- If you have not repaid your loan in full after making the equivalent of 25 years of qualifying monthly payments, any outstanding balance on your loan will be forgiven.
- A student loan payment that will never exceed 15% of your discretionary income.
- The possibility of having a student loan payment of $0.
Cons of the Income-Based Repayment
- You’ll pay more for your loan over time than you would on the 10-Year Standard Plan
- You must have a financial hardship to qualify for this plan.
- If any portion of your loan is forgiven, you may have to pay income tax on the amount.
*You are a new borrower for the IBR plan if you have no outstanding balance on a Direct Loan or Federal Family Education Loan (FFEL) Program loan as of July 1, 2014 or have no outstanding balance on a Direct Loan or FFEL Program loan when you obtain a new loan on or after July 1, 2014.
2. Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan (PAYE)
This plan will help you get a more affordable monthly loan payment based on your income and family size. The PAYE lowers the cap of some student loan bills from 15% to 10% of your discretionary income.
Plan Basics
The Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan calculates your monthly payment based on your income and the size of your family, while not exceeding 10% of your discretionary income.
Time Till Debt Free
20 Years
Loans Eligible for Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans
- Direct PLUS Loans made to graduate or professional students
- Direct Consolidation Loans that don’t include repaying Plus loans made to parents
- Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans (made under the FFEL Program)
- Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans (made under the FFEL program)
- FFEL PLUS Loans for graduate and professional students
- FFEL Consolidation Loans that didn’t repay any PLUS loans made to parents
- Federal Perkins Loans (*if they are consolidated)
Monthly Payments
Your payment is calculated by taking 10% of the difference between your adjusted gross income (AGI) and 150% the poverty level for your state and family size.
Your payments change as your income changes.
Pros of the Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan
- Your monthly payments will be lower than they would be on the Standard Repayment Plan.
- If you have not repaid your loan in full after you made the equivalent of 20 years of qualifying monthly payments, any outstanding balance on your loan will be forgiven.
- The possibility of having a student loan payment of $0.
- A student loan payment that never exceeds 10% of your discretionary income.
Cons of the Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan
- You must have a financial hardship to qualify for this plan.
- You’ll pay more for your loan over time than you would under the 10-Year Standard Repayment Plan.
- You may have to pay income tax on any amount that is forgiven.
3. Income-Contingent Repayment Plan (ICR)
This plan can help you get a more affordable monthly payment that is based off of your income and the size of your student loan debt, or a payment that is based solely off income.
Plan Basics
The Income-Contingent Repayment Plan calculates your monthly payment by taking the lower amount of two calculation methods:
- Based on income and student loan debt
- Based on income alone
No matter what, you’ll never be paying more than 20% of your discretionary income.
Time Till Debt Free
25 Years
Loans Eligible for Income-Contingent Repayment Plan
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans
- Direct PLUS Loans made to graduate or professional students
- Direct Consolidation Loans that don’t include repaying Plus loans made to parents
- Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans made under the FFEL Program (*if they are consolidated)
- Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans made under the FFEL program (*if they are consolidated)
- FFEL PLUS Loans for graduate and professional students (*if they are consolidated)
- FFEL Consolidation Loans that didn’t repay any PLUS loans made to parents (*if they are consolidated)
- FFEL Consolidation Loans that repaid PLUS loans taken out by parents (*if they are consolidated)
- Federal Perkins Loans (*if they are consolidated)
- Direct PLUS Loans taken out by parents (*if they are consolidated)
Monthly Payments
Payments are calculated each year and are based on your adjusted gross income, family size, and the total amount of your Direct Loans.
Your payments change as your income changes.
Pros of the Income-Contingent Repayment Plan
- If you do not repay your loan after making the equivalent of 25 years of qualifying monthly payments, the unpaid portion will be forgiven.
- A student loan payment that never exceeds 20% of your discretionary income.
Cons of the Income-Contingent Repayment Plan
- You’ll pay more for your loan over time than under the 10-Year Standard Plan.
- You may have to pay income tax on the amount of the loan that is forgiven.
- You must be considered to have a partial financial hardship in order to qualify for this loan.
4. Revised Pay As Your Earn Repayment Plan (REPAYE)
UPDATE: THE REPAYE IS NO LONGER ACTIVE PLAN
This plan is an extension of the Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan. It’ll give you a monthly student loan payment that is based off of income and family size.
Plan Basics
The Revised Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan gives you a monthly student loan payment that is based off of income and family size.
No matter what, you’ll never be paying more than 10% of your discretionary income.
Time Till Debt Free
20-25 Years
Loans Eligible for Revised Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans
- Direct PLUS Loans made to graduate or professional students
- Direct Consolidation Loans that didn’t repay Plus loans made to parents
- Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans made under the FFEL Program (*if they are consolidated)
- Unsubsidized Federal Stafford Loans made under the FFEL program (*if they are consolidated)
- FFEL PLUS Loans for graduate and professional students (*if they are consolidated)
- FFEL Consolidation Loans that didn’t repay any PLUS loans made to parents (*if they are consolidated)
- Federal Perkins Loans (*if they are consolidated)
Monthly Payments
Your monthly payment will be capped at 10% of your discretionary income.
Depending on your financial situation, this amount can go up, down or stay the same each year.
Pros of the Revised Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan
- A student loan payment that never exceeds 10% of your discretionary income.
- You don’t have to pay any interest not covered by your monthly payments for the first three years in the repayment plan
- The possibility of having the remainder of your student loan balance forgiven after 20 to 25 years of consecutive payments
Cons of the Revised Pay As You Earn Repayment Plan
- If your income increases significantly over time, it’s possible to have a payment that is higher than the Standard Repayment Plan.
- Due to the longer payment period, you may pay more in interest over the repayment period than under other repayment plans.
- You may have to pay income tax on the amount of the loan that is forgiven.
5. Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE) Repayment Plan
Plan Basics
The SAVE Repayment Plan sets monthly student loan payments based on the borrower’s income and family size. Payments are typically 5-10% of the borrower’s discretionary income, which is calculated as the difference between the borrower’s annual income and 150% of the poverty guideline for their family size and state of residence.
Time Till Debt Free
- 20 years for undergraduate loans
- 25 years for graduate or professional study loans
Loans Eligible for the SAVE Plan
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans
- Direct PLUS Loans made to students
- Direct Consolidation Loans (excluding Direct PLUS Loans made to parents)
Monthly Payments
Your monthly payment will be capped at 5-10% of your discretionary income. This amount can fluctuate based on changes in your financial situation each year.
Pros of the SAVE Repayment Plan
- Payments are tied to income, ensuring affordability.
- After 20-25 years of qualifying payments, any remaining loan balance may be forgiven.
- If monthly payments do not cover accruing interest, the government will pay the remaining interest for certain types of loans for a specified period.
Cons of the SAVE Repayment Plan
- Payments may increase if your income rises significantly over time.
- You may pay more in interest over the extended repayment period compared to shorter-term plans.
- The forgiven loan amount may be subject to income tax.
Annual Recertification
Borrowers need to recertify their income and family size annually. Failure to recertify can result in payments reverting to the Standard Repayment Plan amounts, and any unpaid interest may be capitalized (added to the loan principal).
Contact us at US Student Loan Center at 813.775.2058 if you would like to discuss your repayment plan options with one of our professional and friendly student loan counselors.
Top FAQ About Student Loan Repayment Plans
Q: Can I change student loan repayment plans?
You will be assigned a repayment plan after graduation, but you can change your plan at any time and at no cost to you.
Q: How do I select a student loan repayment plan?
Choosing the right repayment plan for you will depend on your needs and goals. If you want to pay the lowest amount of interest, standard repayment will make the most sense for you. If you need lower payments or qualify for student loan forgiveness, income-driven repayment will be a more suitable option.
Q: What student loan repayment plan am I on?
You can call your loan servicer at any time to find out about the plan that you are on, and other plan options that are available to you.
Q: What is the best student loan repayment plan for married couples?
For Income-Based Repayment (IBR) plans and Pay As You Earn (PAYE) plans, your payments are calculated using your Adjusted Gross Income. If you are married and are looking for lower payments on either of these types of repayment plans, you can file your taxes as “married, filing separately,” so that both incomes are not considered when calculating your payments. However, by filing separately, you will pay more in taxes.
However, if your dual-income household income is high enough and you filed jointly, you will not qualify for IBR or PAYE. An Extended Repayment Plan will give lower payments over a longer period of time. The Standard Repayment Plan will allow you to pay less interest and pay your loans off in a shorter amount of time.
Q: What is the best student loan repayment plan for low income earners?
If you need a low monthly payment, you will want to choose an income-driven repayment plan. There are 4 options: Income-Based Repayment, Income-Contingent Repayment, Pay As You Earn (PAYE) and Revised Pay as You Earn (REPAYE). If you expect your income to increase significantly in the future, you will want to switch back to the Standard Repayment Plan or a Graduated Repayment Plan.
Q: What is the best student loan repayment plan for teachers?
Teachers qualify for student loan forgiveness after 10 years of continuous employment, so your best choice is an income-driven repayment plan. You will pay the least amount before the balance is forgiven.
Q: What is the best student loan repayment plan for PSLF?
Public Service Loan Forgiveness allows graduates in certain professions to have their loan balances forgiven after 10 years in public service. Your best option during that time is an income-driven repayment plan that allows you to pay the lowest amount over the 10 years.
Up Next:


I am wondering when my son has to start repaying his loans. I have not received any mail or email of a payment date. How do I find out his loan number?
I cant afford my payments i.need some help
I was really interesting on your plan.